Ningbo Fenghua Fuyin Auto Cage Accessory Factory
Excellent and stable product quality
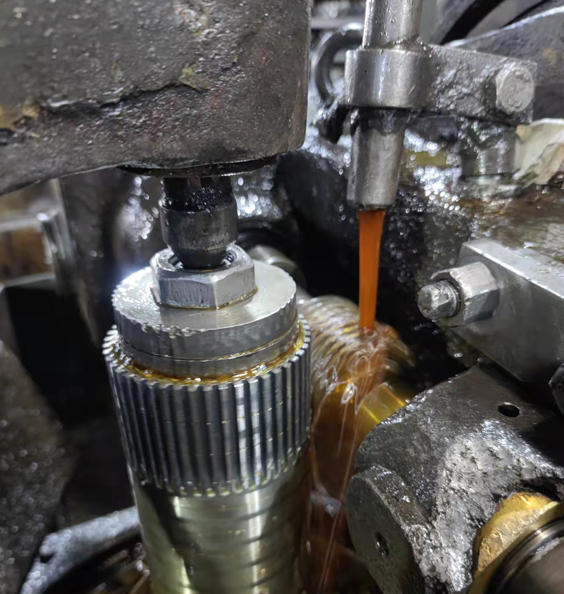
Ningbo Fenghua Fuyin Auto Cage Accessory Factory is China Gear manufacturers and OEM Gear factory. Fenghua Fuyin is the first batch of factories that started to produce ABS gear rings in China, until now its almost 30 years. We accept OEM&ODM, your drawings or samples are quite welcome. Our products mainly applied to car brands not only including Germany, Japan, and the United States, such as BMW, Audi, Mazda, Ford, and Volkswagen, but also domestic car brands such as Changan, Jianghuai, Geely, BAIC, and Hezhong. Our wholesale Gear have excellent quality and conform to the environmental standards of Europe and America, which can be used for trucks, traditional fuel passenger cars, and new energy vehicles.

 English
English 中文简体
中文简体





 +86-18352944301
+86-18352944301 +86-13003719355
+86-13003719355 info@xring-autoparts.com
info@xring-autoparts.com